Earthquakes happen on the earth were ever there has been enough stored up elastic strain energy to drive factures along a fault plane. As the plates are moving past each other sometimes they lock and this causes them to build up tension until they finally force past each other and cause shaking or earthquakes. When this happens within the continental lithosphere sometimes the plate deformation is spread out over a larger area then the plate boundary itself. The earthquakes away from the plate boundaries are caused by the fact that strain occurs in these continental deformation.
2. Normal Fault:

 Reverse Fault:
Reverse Fault:
Overthrust Fault:
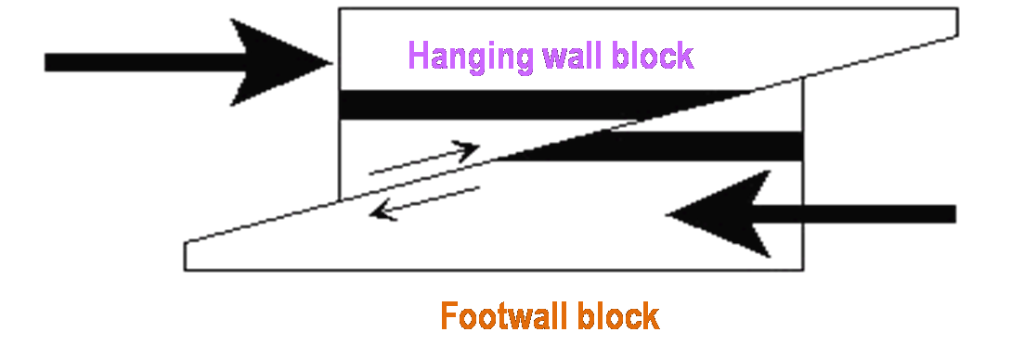
Transform Fault:
 3. Describe the dangers associated with earthquakes.
3. Describe the dangers associated with earthquakes.The effects of earthquakes are many including:
Shaking and Ground Rupture: Depending on the strength of the earthquake and how close you are to the epicenter this will have different effects. Sometimes you may just feel minor shaking and other times whole cities can be destroyed. On occasion there is visible breaking of the earths surface, which could cause severe damage as well. Most of the time however they have learned where this breaking would occur and make sure to build nothing major in these areas.
Landslides and Avalanches: On steep slopes earthquakes can often cause rock and snow to fall and collect taking anything in its path with it.
Fires: Because of the fact that it causes the earth to shake if often causes power lines to break and this can cause fires in large cities.
Soil Liquefaction: Because of the shaking of the earth it can sometimes cause solid ground material to turn to more of a liquid, and this can cause buildings to sink.
Tsunami: When there are large earthquakes under the ocean it causes large, long period waves to come to the surface. Where there are cities near the ocean this can be devastating.
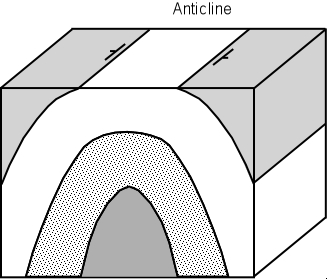
4. Anticline:
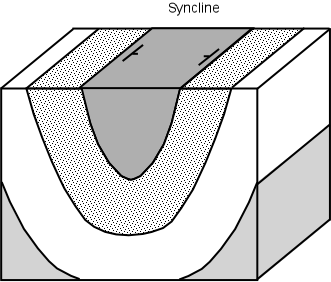
Syncline:
Dome:

Geosyncline:

